accumulated earnings tax calculation
The regular corporate income tax. 25000 250000 Accumulated EP at.
When the revenues or profits are above this level the firm will be subjected to accumulated earnings tax if they do not distribute the dividends to shareholders.
. The Portfolio outlines in detail the statutory framework of the accumulated earnings tax the factors used to determine whether a. Multiply each 4000 distribution by the 0625 figured in 1 to get the amount 2500 of each distribution treated as a distribution of current year earnings and profits. 531 and 532.
The tax rate is 20 of accumulated taxable in-come defined as taxable income with adjustments including the subtraction of federal and foreign income taxes. 796 analyzes in detail the problems associated with a corporations failure to distribute its earnings and profits with the purpose of avoiding the tax on its shareholders. Computing the Accumulated Earnings Tax.
Breaking Down Accumulated Earnings Tax. Accumulated Earnings Tax can be reduced by reducing Accumulated Taxable Income. The result is 0625.
If a C corporation retains earnings doesnt distribute them to shareholders above a certain amount an amount which the IRS concludes is beyond the reasonable needs of the business the corporation may be assessed tax penalty called the accumulated earnings tax IRC section 531 equal to 20 percent 15 prior to 2013 of accumulated taxable income. 2 The determination of EP for any given year generally starts with the companys final adjusted taxable income for that year taking into account the taxable income reported on the originally filed corporate tax return and any. Ad No Matter What Your Tax Situation Is TurboTax Has You Covered.
The tax is in addition to the regular corporate income tax and is assessed by the IRS typically during an IRS audit. There is a certain level in which the number of earnings of C corporations can get. The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20 the maximum rate at which they would.
Ad Free tax support and direct deposit. The accumulated earnings tax also called the accumulated profits tax is a tax on abnormally high levels of earnings retained by a company. The Accumulated Earnings Tax is computed by multiplying the Accumulated Taxable Income IRC Section 535 by 20.
Divide the current year earnings and profits 10000 by the total amount of distributions made during the year 16000. Ad Determine Working Capital Needs with the Bardahl Formula. Bloomberg Tax Portfolio Accumulated Earnings Tax No.
The threshold is 25000 without accumulated earning tax. Determining a stand-alone corporations EP takes into account the financial transaction and tax return information for the company since its inception. The accumulated earnings tax may be imposed on a corporation for a tax year if it is determined that the corporation has attempted.
This tax evolved as shareholders began electing to have companies retain earnings rather than pay them out as dividends in an effort to avoid high levels of taxation. Divide the current year earnings and profits 10000 by the total amount of distributions made during the year 16000. The accumulated earnings tax also called the accumulated profits tax is a tax on abnormally high levels of earnings retained by a company.
Helping You Avoid Confusion This Tax Season. The Accumulated Earnings Tax is more like a penalty since it is assessed by the IRS often years after the income tax return was filed. 8 rows Calculate Tax.
The accumulated earnings tax imposed by section 531 shall apply to every corporation other than those described in subsection b formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax with respect to its shareholders or the shareholders of any other corporation by permitting earnings and profits to accumulate instead of being divided or distributed. The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20 the maximum rate at which they would be taxed if distributed. IRC Section 535c1 provides that.
A corporation may be allowed an accumulated earnings credit in the na-ture of a deduction in computing accu-mulated taxable income to the extent it. TAX CASE As the difference between ordinary income tax rates and capital gains tax rates increases corporations have sought to minimize dividend payments to shareholders with the objective of helping them secure capital gains taxed at a lower rate. The purpose of the accumulated earnings tax is to compel.
To prevent companies from doing this Congress adopted the excess accumulated. Try Our Free Tax Refund Calculator Today. The accumulated earnings tax is imposed on the accumulated taxable income of every corporation formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax with respect to its shareholders by permitting earnings and profits to accumulate instead of being divided or distributed.
The AET is a penalty tax imposed on corporations for unreasonably accumulating earnings. It compensates for taxes which cannot be levied on dividends.

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part I

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part Ii

Understanding The Accumulated Earnings Tax Before Switching To A C Corporation In 2019

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study
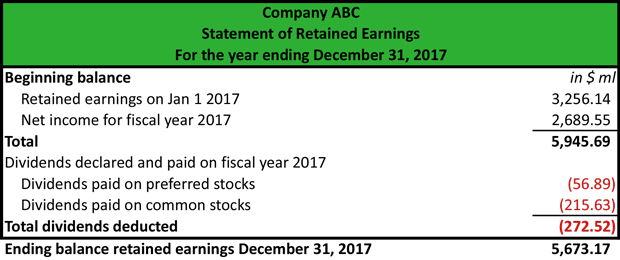
What Are Accumulated Earnings Definition Meaning Example

Income Tax Computation Corporate Taxpayer 1 2 What Is A Corporation Corporation Is An Artificial Being Created By Law Having The Rights Of Succession Ppt Download

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part Ii
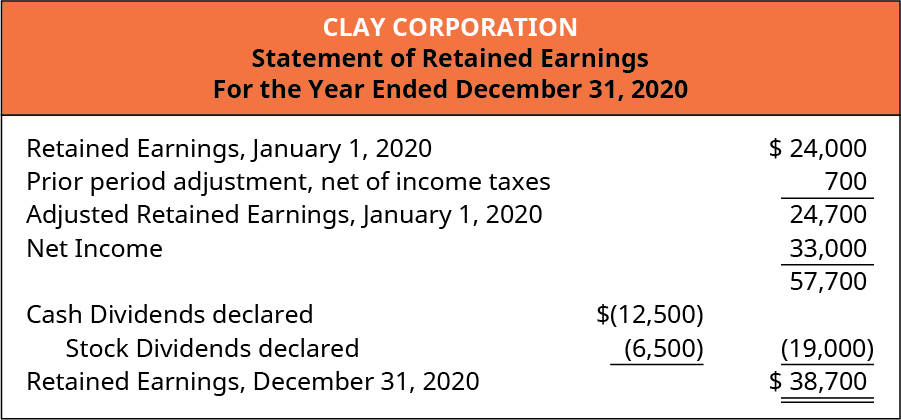
Compare And Contrast Owners Equity Versus Retained Earnings Principles Of Accounting Volume 1 Financial Accounting

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

What Are Earnings After Tax Bdc Ca


